 风湿消息
风湿消息
Rheumatology & Autoimmunity | 2023年第4期,欢迎阅读引用
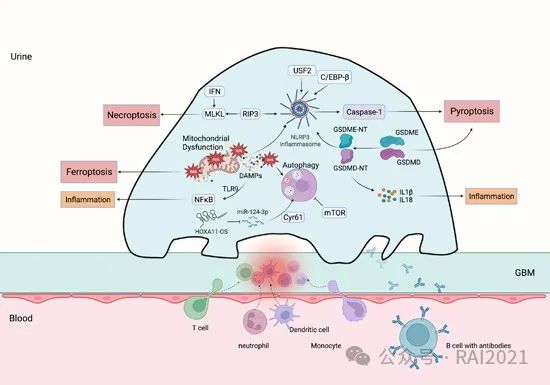
Podocyte injury and death: New insights into lupus nephritis pathogenesis and therapy
Xiaolei Shi, Zhipeng Wang, Ruihan Tang, Wei Chen
本文对足细胞功能障碍及其在狼疮性肾炎(LN)发生、发展中的作用以及针对足细胞的治疗策略进行综述。自噬和线粒体功能障碍是细胞周转的关键,而在某些情况下,它们会导致足细胞损伤或丢失。由于缺乏关于LN足细胞发生铁死亡的具体证据,因此需要更多的研究结果来明确LN足细胞功能障碍。这些通路的初步研究结果表明,它们具有作为LN临床治疗潜在靶点的价值。
How to cite: Shi
(扫码阅读全文)
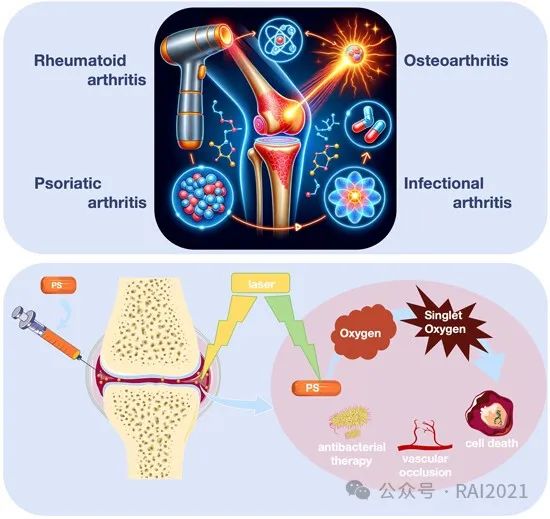
Photodynamic therapy for arthritis: a promising therapeutic strategy
Liangyu Mi, Jinfang Gao, Ying Liu, Na Zhang, Miaomiao Zhao, Sheng Wang, Ke Xu
(扫码阅读全文)
点击链接查看推文:RAI | 光动力疗法治疗关节炎:有前景的治疗策略
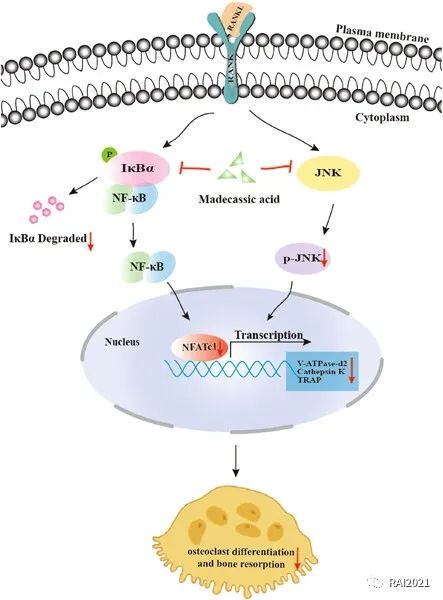
Madecassic acid suppresses osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by inhibiting RANKL-induced NF-κB, JNK and NFAT signaling pathways
本实验用核因子受体活化因子(NK-κΒ)配体刺激RAW 264.7细胞向多核破骨细胞分化。随后加入不同浓度(1、2.5、5、10 μmol/L)的羟基积雪草酸处理破骨细胞。结果显示,羟基积雪草酸通过抑制NF-κB、JNK和NFAT信号通路抑制破骨细胞的形成和功能,有望成为治疗破骨细胞相关骨病尤其是骨质疏松症的新型药物。
How to cite: Su
(扫码阅读全文)
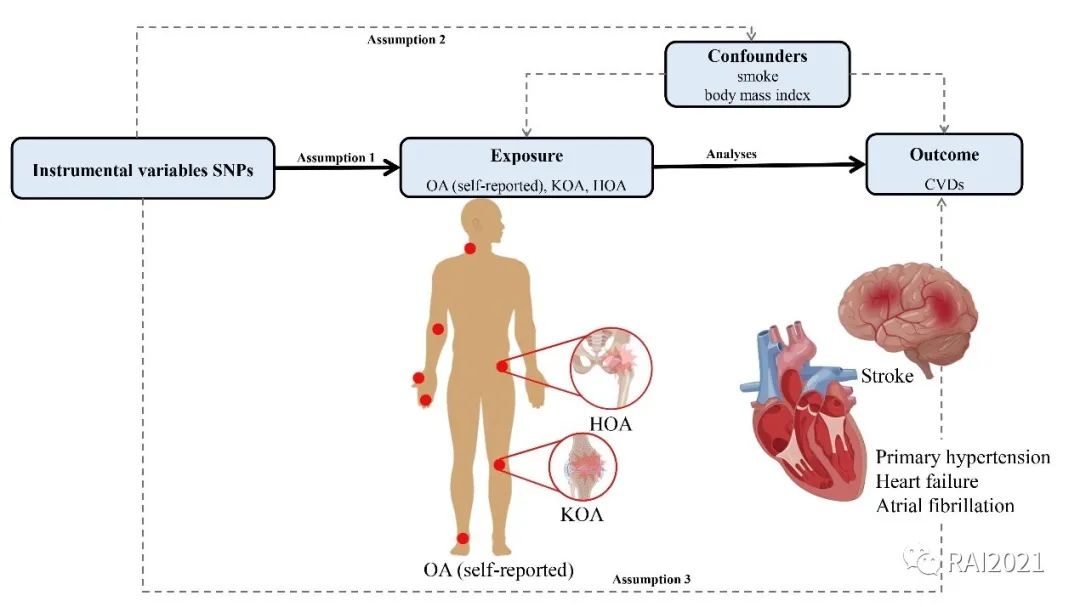
Genetic evidence suggesting the predicted causality between osteoarthritis and cardiovascular diseases
Shengxiao Zhang, Yige Feng, Xinyu Yin, Qinyi Su, Yujia Xi, Ting Cheng, Heyi Zhang, Yulong Xue, Caihong Wang, Xiaofeng Li
本文通过双样本孟德尔随机化(MR)研究,探索骨关节炎(OA)与心血管疾病(CVD)之间的潜在因果关系。结果提示OA增加了卒中、原发性高血压、心力衰竭和心房颤动的发病率,并且这种影响在身体的不同部位存在差异。医疗保健专业人员需要管理OA患者的心血管危险因素。
How to cite: Zhang S, Feng Y, Yin X, et al. Genetic evidence suggesting the predicted causality between osteoarthritis and cardiovascular diseases. Rheumatol & Autoimmun. 2023; 3: 230-239. doi:10.1002/rai2.12097
(扫码阅读全文)
点击链接查看推文:RAI | 遗传证据表明骨关节炎和心血管疾病存在因果关系
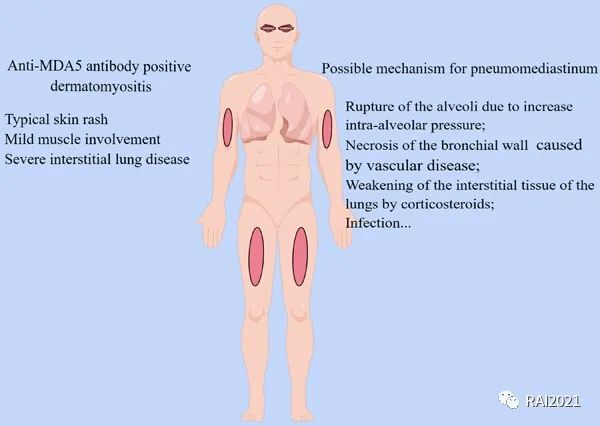
Successful treatment of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease complicated by a refractory pneumomediastinum in a patient with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis
Lili Jiang, Hong Chen, Lihua Duan
自发性纵隔气肿是抗黑色素瘤分化相关基因5阳性(抗-MDA5)皮肌炎的一种相对少见但严重的并发症,增加了其死亡率。本文报道了一例53岁的抗-MDA5型糖尿病患者,其表现为快速进展的间质性肺疾病,尽管进行了积极的免疫抑制治疗,但仍进展为弥漫性皮下肺气肿和自发性纵隔气肿。经抗感染、适度免疫、持续氧疗等综合治疗,患者反应良好。对潜在感染的全面筛查以及密切监测患者的免疫状态对于个体化治疗和最大限度地改善预后至关重要。
How to cite: Jiang L, Chen H, Duan L. Successful treatment of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease complicated by a refractory pneumomediastinum in a patient with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatol & Autoimmun. 2023; 3: 240-243. doi:10.1002/rai2.12079
(扫码阅读全文)
Coexistent ankylosing spondylitis and intellectual developmental disorder with behavioral abnormalities and craniofacial dysmorphism with or without seizures
Weizhen Xiang, Min Fu, Zhenzhen Ma, Qingrui Yang
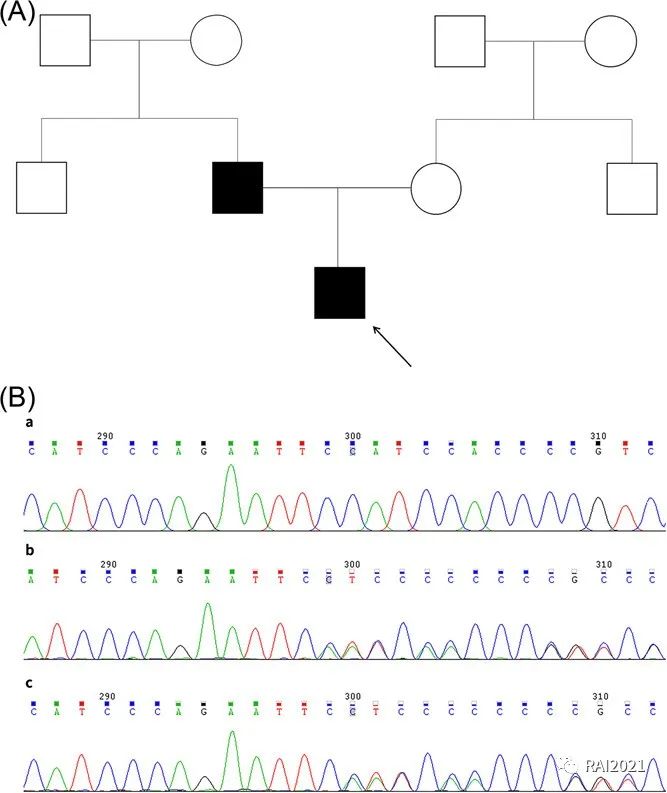
(扫码阅读全文)
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults associated with COVID-19: A rare life-threatening complication
Sameen Zafar, Daniel Gonzalez, Leonard Kuan-Pei Wang, Alexandria Soybel, Emilio B. Gonzalez, Vijaya Murthy
本病例强调在对SARS-CoV-2感染患者进行单克隆抗体输注治疗后出现全身症状的患者进行评估时,在早期评估时将成人多系统炎症综合征纳入鉴别诊断的考虑是必要的,以便及时诊断和治疗。
How to cite: Zafar S, Gonzalez D, Wang LK-P, Soybel A, Gonzalez EB, Murthy V. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults associated with COVID-19: a rare life-threatening complication. Rheumatol & Autoimmun. 2023; 3: 247-249. doi:10.1002/rai2.12094
(扫码阅读全文)
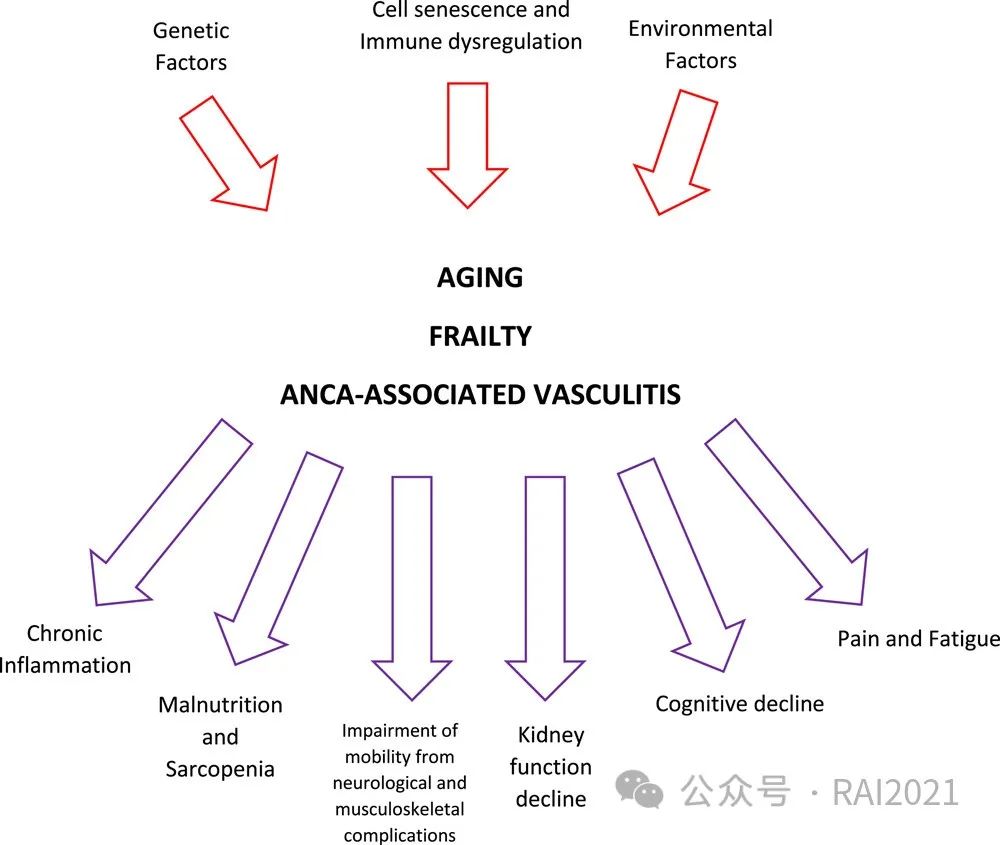
Frailty and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: What do we know?
Henry H. L. Wu, Nina Brown, Rajkumar Chinnadurai
How to cite: Wu, H.H.L., Brown, N. and Chinnadurai, R. (2023), Frailty and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: What do we know?. Rheumatology & Autoimmunity, 3: 250-252. https://doi.org/10.1002/rai2.12098
(扫码阅读全文)
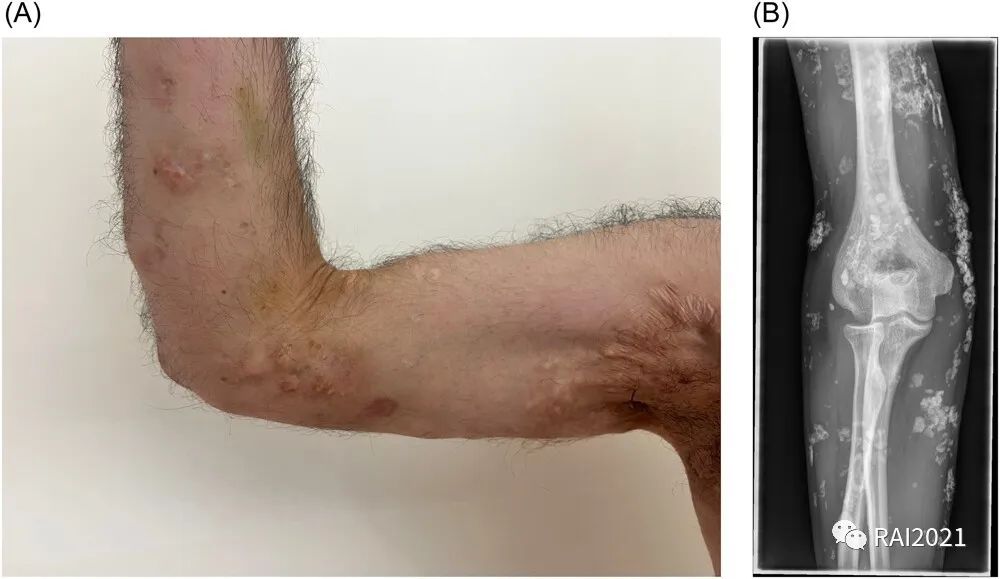
Calcinosis cutis in a young man with dermatomyositis
Marco Krasselt, Jeanette Henkelmann, Matthias Pierer
本文报告了一名25岁患有多发性肌炎的男性。实验室检查显示C-反应蛋白和肌酸激酶升高,抗核抗体、抗Mi-2抗体、抗Jo-1抗体和抗Scl-70抗体为阴性,风湿因子为阳性。甲襞微循环检查显示大量树状分支的毛细血管,反映了多发性肌炎典型的新生血管形成。体格检查显示上肢、下肢和躯干广泛的皮肤钙质沉着症。患者长期以来仅接受泼尼松治疗,为减少激素副作用,开始使用硫唑嘌呤免疫抑制治疗,但对皮肤钙化无显著改善。文章讨论了多发性肌炎患者罕见的皮肤钙化症状及其治疗挑战。
How to cite: Krasselt M, Henkelmann J, Pierer M. Calcinosis cutis in a young man with dermatomyositis. Rheumatol & Autoimmun. 2023; 3: 253-254. doi:10.1002/rai2.12092
(扫码阅读全文)
Outer membrane vesicles from Fusobacterium nucleatum aggravate rheumatoid arthritis
Ru Li
有研究发现,在类风湿性关节炎(RA)中,肠道微生物与滑膜免疫之间存在新的相互作用方式。研究揭示了具核梭杆菌(F. nucleatum)及其外膜囊泡(OMVs)在RA炎症中的关键作用。通过16S rRNA测序,临床研究和体内模型,研究者发现F. nucleatum在RA患者中富集,并与疾病活动正相关。实验表明F. nucleatum通过分泌OMVs促进关节炎。F.n分泌的OMVs增强了 Rab5a 和 YB-1 之间的相互作用,从而促进了 YB-1 的磷酸化和核易位。其通过靶向Rab5a-YB-1轴在加重RA中起因果作用。这一发现为深入了解RA发病机制提供了重要线索,将F. nucleatum和其OMVs作为治疗RA的潜在靶点。
How to cite: Li, R. (2023), Outer membrane vesicles from Fusobacterium nucleatum aggravate rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology & Autoimmunity, 3: 255-256. https://doi.org/10.1002/rai2.12093
(扫码阅读全文)
Rheumatology & Autoimmunity是由中华医学会主办、中华医学杂志社与Wiley合作出版发行的全英文风湿病与免疫学专业期刊,发表风湿病与免疫学领域中临床诊治、转化及基础研究方面的新进展。涵盖风湿病学和免疫学的各个领域,旨在为国内外相关领域科学家与临床专家提供一个学术交流、信息传递的平台,同时提升我国风湿病与免疫学在国际学术界的影响力和竞争力。
期刊发表范围
涵盖风湿病学和临床免疫学的各个领域,包括各种风湿病、自身免疫病以及免疫学基础及转化医学研究。
感兴趣的主题
各种风湿病和自身免疫病的基础和临床研究,包括但不限于以下疾病:
• Rheumatoid Arthritis
类风湿关节炎
• Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
系统性红斑狼疮
• Sjogren Syndrome
干燥综合征
• Spondyloarthritis
脊柱关节炎
• Gout
痛风
• Osteoarthritis
骨关节炎
• Psoriatic Arthritis
银屑病关节炎
• Inflammatory Myopathy
炎性肌病
• Systematic Sclerosis
系统性硬化症
• Systemic Vasculitis
系统性血管炎

版权所有 © 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫研究所
技术支持:优河马