
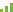 风湿消息
风湿消息
RA研究新高度 | 类风湿关节炎年度精选合集 (2024-2025)
关注RAI | 共创未来
Rheumatol
Autoimmun

导读
Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
类风湿关节炎(RA)研究迎来新突破!本期特别整理2024–2025年度RA领域代表性研究成果,聚焦人工智能、潜在药物、发病机制与生物信息学等多个前沿方向。从智能技术赋能RA诊疗,到关键靶点与信号通路的深入挖掘,这些研究不仅展现了基础科研的深度,也为临床转化提供了新思路。
1
【Review】Artificial intelligence in rheumatoid arthritis
Yiduo Sun, Jin Lin, Weiqian Chen

How to cite: Sun Y, Lin J, Chen W. Artificial intelligence in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2025; 5: 88–100. doi:10.1002/rai2.12171
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)
2
【Review】Artificial intelligence in rheumatoid arthritis research: A bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2023
Yang Liu, Yazhen Su, Zewen Wu, Jinfang Gao, Xueyan Gong, Liyun Zhang
How to cite: Liu Y, Su Y, Wu Z, Gao J, Gong X, Zhang L. Artificial intelligence in rheumatoid arthritis research: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2023. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2024; 4: 133-144. doi: 10.1002/rai2.12142
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)
3
【Review】Matrine, a potential drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Yaping Peng, Xinqiao Lian, Yan Wang, Xin Li

How to cite: Peng Y, Lian X, Wang Y, Li X. Matrine, a potential drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2024; 4: 11-19. doi: 10.1002/rai2.12111
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)
4
【Original Article】Pathologically expanded peripheral CD4+PD-1+Foxp3− T-cell subset promotes B-cell hyperactivity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Ziran Bai, Rui Liu, Jiaqing Liu, Cheng Zhang, Zilong Wang, Jingjing Qi, Yawei Tang, Xia Li

How to cite: Bai Z, Liu R, Liu J, et al. Pathologically expanded peripheral CD4+PD-1+Foxp3− T-cell subset promotes B-cell hyperactivity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2024; 4: 27-36. doi: 10.1002/rai2.12114
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)
5
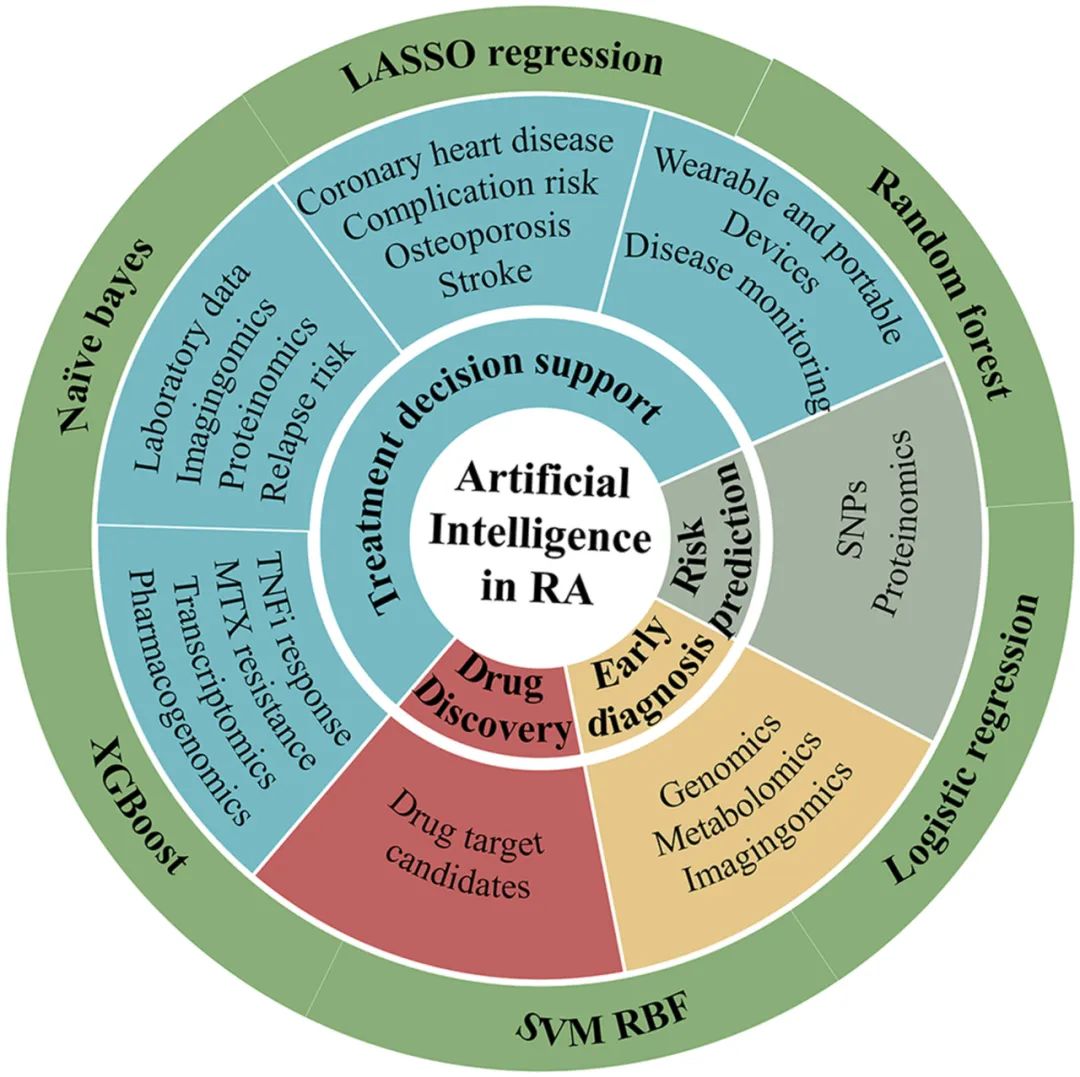
【Original Article】SLAMF8 as a potential biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis identified by comparing peripheral blood mononuclear cells, fibroblast‐like synoviocytes, and synovial tissue using bioinformatics analysis
Cheng Zhang, Huina Huang, Jie Zhang, Yifan Huang, Yuanhua Qin, Xia Li, Guan Wang
How to cite: Zhang C, Huang H, Zhang J, et al. SLAMF8 as a potential biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis identified by comparing peripheral blood mononuclear cells, fibroblast-like synoviocytes, and synovial tissue using bioinformatics analysis. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2024; 4: 99-108. doi: 10.1002/rai2.12117
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)
6
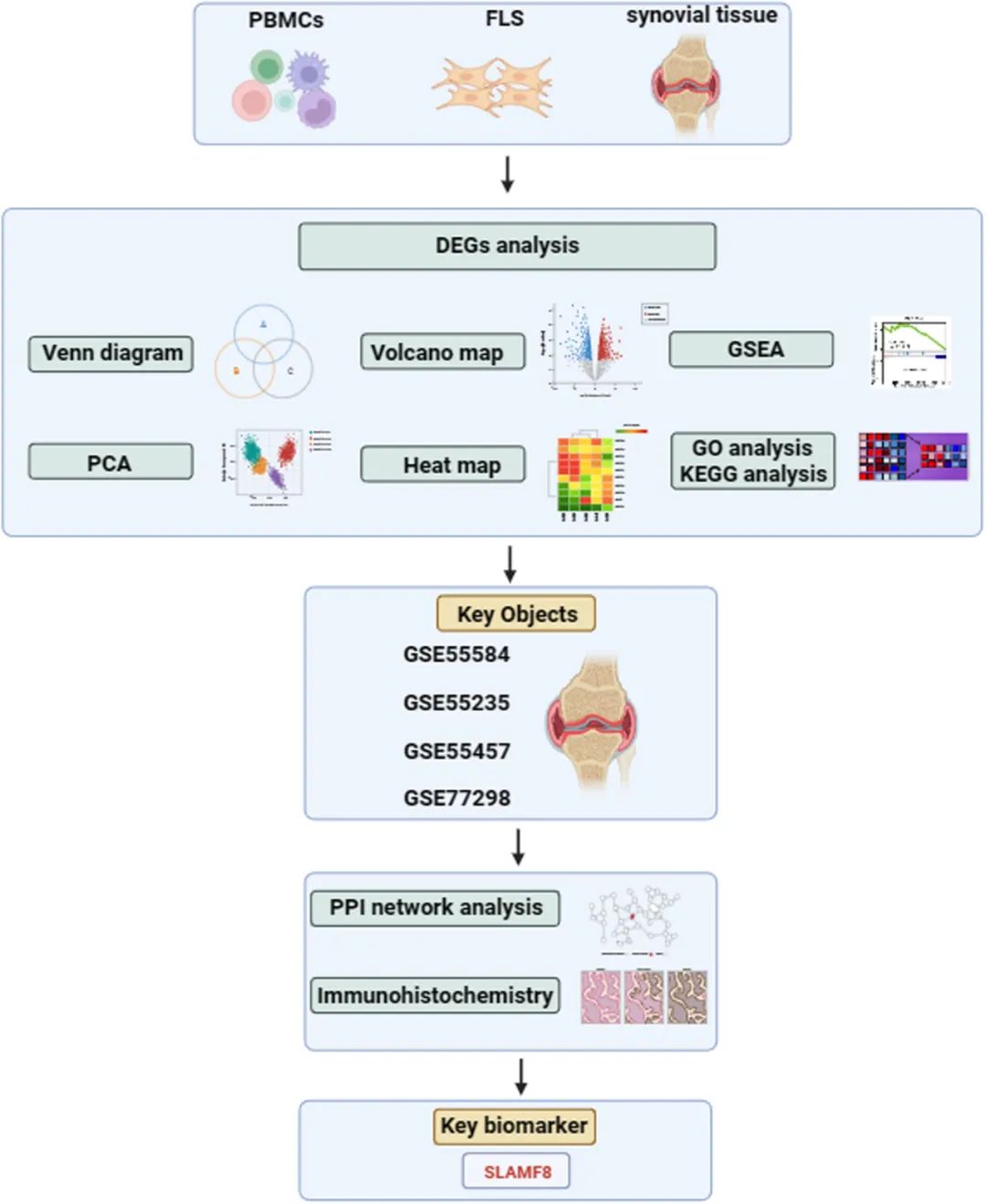
【Original Article】Rapamycin suppresses rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast synovial cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via the AKT/mTORC1 pathway
Shengxiao Zhang, Xiaorong Hu, Qinyi Su, Heyi Zhang, Ting Cheng, Jia Wang,Ruomeng Pei, Xin Li, Ruqi Zhang, Hongfang Shao, Caihong Wang, Xiaofeng Li
How to cite: Zhang S, Hu X, Su Q, et al. Rapamycin suppresses rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast synovial cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via the AKT/mTORC1 pathway. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2024; 4: 156-164. doi: 10.1002/rai2.12120
Article link:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/rai2.12120

(扫码阅读全文)
7
【Original Article】Genetically supported causal genes for rheumatoid arthritis: Mendelian randomization and co-localization analyses
Yuanyuan Niu, Fan Su, Simin Chen, Jingnan Wang, Shuoyang Zhang, Ruiru Li, Yu Kuang, Liuqin Liang, Youjun Xiao, Hanshi Xu

How to cite: Niu Y, Su F, Chen S, et al. Genetically supported causal genes for rheumatoid arthritis: Mendelian randomization and co-localization analyses. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2024; 4: 242-253. doi: 10.1002/rai2.12145
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)
8
【Original Article】Inverse association between serum Klotho levels and rheumatoid arthritis risk: Insights from the NHANES database
Qianqian Xu, Jianpeng Yu, Jiaqi Hu, Xia Xu, Lanling Zhang, Qian Chen, Jie Gao

How to cite: Xu Q, Yu J, Hu J, et al. Inverse association between serum Klotho levels and rheumatoid arthritis risk: insights from the NHANES database. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2025; 5: 64-70. doi:10.1002/rai2.12170
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)
9
【Letter to the Editor】Expression of SALL4 in the synovial tissue of refractory rheumatoid arthritis patients
Ru Fan, Zeqiong Liang, Yujie Bu, Fen Zhang, Xing Cen, Yuqing Liu, Fenping Lian, Fengwu Chen, Shengxiao Zhang, Junwei Chen

How to cite: Fan R, Liang Z, Bu Y, Zhang F, Cen X, Liu Y, et al. Expression of SALL4 in the synovial tissue of refractory rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2024; 4: 59-61. doi: 10.1002/rai2.12109
Article link:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/rai2.12109

(扫码阅读全文)
10
【Letter to the Editor】Assessment of factors influencing outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.5.2/BF.7 infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients
Yan Wang, Mengyao Zhang, Sitian Zang, Liang Luo, Chun Li, Jing He, Zhanguo Li
How to cite: Wang Y, Zhang M, Zang S, et al. Assessment of factors influencing outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.5.2/BF.7 infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Autoimmun 2025; 5: 157-159. doi:10.1002/rai2.70004
Article link:

(扫码阅读全文)

RAI 简 介
期刊主页:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/27671429
投稿网址:
https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/rai
邮箱:rai@cmaph.org
电话:010-51322118
地址:北京市西城区东河沿街69号正弘大厦427室
版权所有 © 北京大学人民医院风湿免疫研究所
技术支持:优河马










